pthread.h 接口封装
项目地址: github.com/AaronComo/OS-Assignment
静态封装 pthread.h
- 由
pthread.h提供的线程库过于繁杂, 使用不同函数创建线程需要大量重复工作, 且pthread_create()函数对函数定义提出了明确的形式化规定, 可扩展性极差. - 故将
pthread.h封装为thread.h, 提供如下API:int create(void *func);void wait(int id);
- 使用
void *wrapper(void *arg);作为函数封装器, 使不同函数均可使用提供的接口.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
#ifndef __THREAD_H__
#define __THREAD_H__
#include <pthread.h>
#include <assert.h>
#endif
#define MAX_THREAD 64
enum { T_FREE = 0, T_ALIVE, T_DEAD };
struct thread {
int id, status; /* id: index in tpool */
pthread_t thread;
pthread_attr_t attr;
void (*entry)(int); /* save entry of exec_func */
};
struct thread tpool[MAX_THREAD], *tptr = tpool;
void *wrapper(void *arg) {
((struct thread *)arg)->entry(((struct thread *)arg)->id);
return NULL;
}
int create(void *func) {
assert(tptr - tpool < MAX_THREAD);
*tptr = (struct thread) {
.id = tptr - tpool,
.status = T_ALIVE,
.entry = func,
};
pthread_attr_init(&(tptr->attr));
pthread_create(&(tptr->thread), &(tptr->attr), wrapper, tptr); /* transfer tptr as params to wrapper */
return (tptr++)->id;
}
void join() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_THREAD; ++i) {
struct thread *t = &tpool[i];
if (t->status == T_ALIVE) {
pthread_join(t->thread, NULL);
t->status = T_DEAD;
}
}
}
void wait(int id) {
pthread_join(tpool[id].thread, NULL);
tpool[id].status = T_DEAD;
}
__attribute__((destructor)) void cleanup() {
join();
}
测试封装线程库
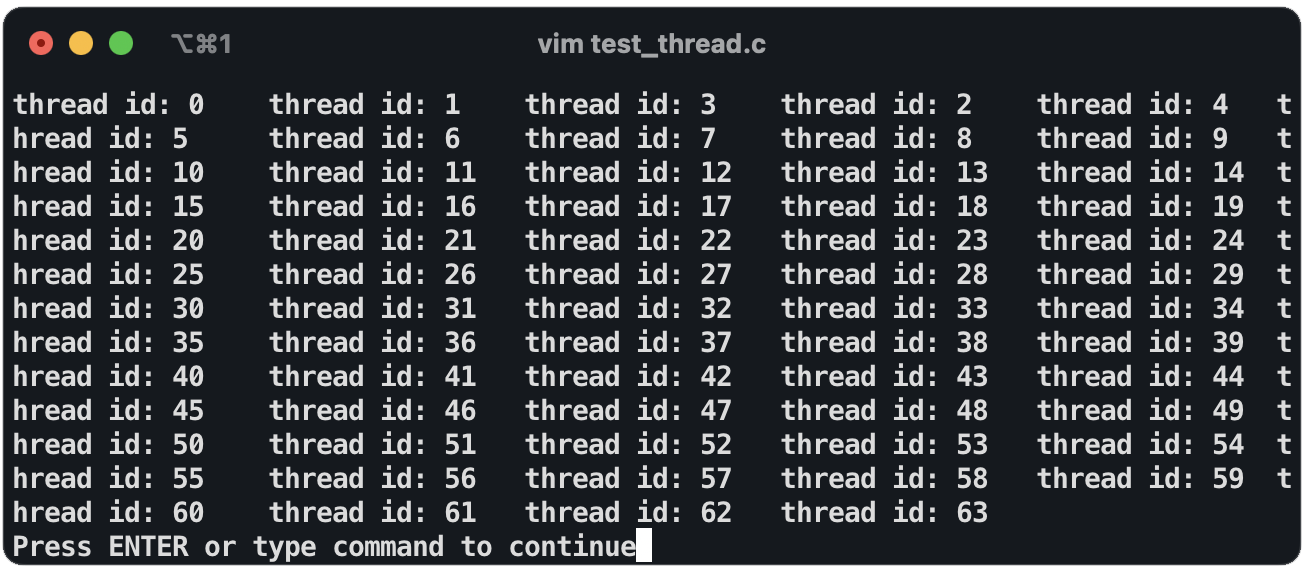
编写测试程序, 创建 64 个线程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
#include <stdio.h> #include "thread.h" void test(int id) { printf("thread id: %d\n", id); } int main() { for (int i = 0; i < MAX_THREAD; ++i) { create(test); } return 0; }
测试结果
程序成功创建64个线程
动态封装
静态封装含有硬编程 #define MAX_THREAD 64, 规定了线程池的最大容量, 不具有可扩展性. 可通过动态分配内存来解决上限问题.
使用动态内存分配的方式为线程池分配空间
宏定义基础块大小
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
#ifndef __THREAD_H__ #define __THREAD_H__ #define BLOCK_SIZE 64 #include <pthread.h> #include <assert.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #endif
编写线程池扩容函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
void __tpool_inflate() { struct thread *p = tpool; p = (struct thread *)calloc(BLOCK_SIZE * (++n), sizeof(struct thread)); if (tpool) { memcpy(p, tpool, (n - 1) * BLOCK_SIZE * sizeof(struct thread)); free(tpool); } tpool = p; tptr = tpool + (n - 1) * BLOCK_SIZE; }
- 容量达到上限
n时, 分配n + 1个块的内存 - 将原内存内容拷贝到新内存
tpool指针指向新内存, 回收旧内存
- 容量达到上限
在构造器中为线程池分配初始空间
1 2 3 4
__attribute__((constructor)) void init() { pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); __tpool_inflate(); }
- 必须使用构造器分配初始内存, 否则后续无法回收
将创建线程函数作为临界区, 加互斥锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
int create(void *func) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if (tptr - tpool >= n * BLOCK_SIZE) { __tpool_inflate(); } *tptr = (struct thread){ .id = (int)(tptr - tpool), .status = T_ALIVE, .entry = (void (*)(int))func, }; pthread_attr_init(&(tptr->attr)); pthread_create(&(tptr->thread), &(tptr->attr), __wrapper, tptr); /* transfer tptr as params to __wrapper */ pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); return (tptr++)->id; }
当线程并发进行扩容与创建时, 可能导致先创建的线程访问到已被回收的内存空间, 导致段错误
对创建过程加锁, 保证互斥访问
析构器等待所有线程执行完成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
void __join() { for (int i = 0; i < n * BLOCK_SIZE; ++i) { struct thread *t = &tpool[i]; if (t->status == T_ALIVE) { pthread_join(t->thread, NULL); t->status = T_DEAD; } } } __attribute__((destructor)) void cleanup() { pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); __join(); }
完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78
#ifndef __THREAD_H__ #define __THREAD_H__ #define BLOCK_SIZE 64 #include <pthread.h> #include <assert.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #endif static int n = 0; pthread_mutex_t mutex; enum { T_FREE = 0, T_ALIVE, T_DEAD }; struct thread { int id, status; /* id: index in tpool */ pthread_t thread; pthread_attr_t attr; void (*entry)(int); /* save entry of exec_func */ }; struct thread *tpool, *tptr; void *__wrapper(void *arg) { ((struct thread *)arg)->entry(((struct thread *)arg)->id); return NULL; } void __tpool_inflate() { struct thread *p = tpool; p = (struct thread *)calloc(BLOCK_SIZE * (++n), sizeof(struct thread)); if (tpool) { memcpy(p, tpool, (n - 1) * BLOCK_SIZE * sizeof(struct thread)); free(tpool); } tpool = p; tptr = tpool + (n - 1) * BLOCK_SIZE; } int create(void *func) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if (tptr - tpool >= n * BLOCK_SIZE) { __tpool_inflate(); } *tptr = (struct thread){ .id = (int)(tptr - tpool), .status = T_ALIVE, .entry = (void (*)(int))func, }; pthread_attr_init(&(tptr->attr)); pthread_create(&(tptr->thread), &(tptr->attr), __wrapper, tptr); /* transfer tptr as params to __wrapper */ pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); return (tptr++)->id; } void __join() { for (int i = 0; i < n * BLOCK_SIZE; ++i) { struct thread *t = &tpool[i]; if (t->status == T_ALIVE) { pthread_join(t->thread, NULL); t->status = T_DEAD; } } } void wait(int id) { pthread_join(tpool[id].thread, NULL); tpool[id].status = T_DEAD; } __attribute__((constructor)) void init() { pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); __tpool_inflate(); } __attribute__((destructor)) void cleanup() { pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); __join(); }
使用 thread_dynamic.h 实现无死锁哲学家就餐问题
创建互斥资源模拟筷子, 创建
direction[]数组表示筷子方位1 2
int direction[2] = { 0, 1 }; pthread_mutex_t chopsticks[5];
创建 5 个哲学家线程, 初始化互斥变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { pthread_mutex_init(&chopsticks[i], NULL); create(philosopher); } return 0; }
编写哲学家线程
1 2 3 4 5 6
void philosopher(int id) { for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { pickup_forks(id); return_forks(id); } }
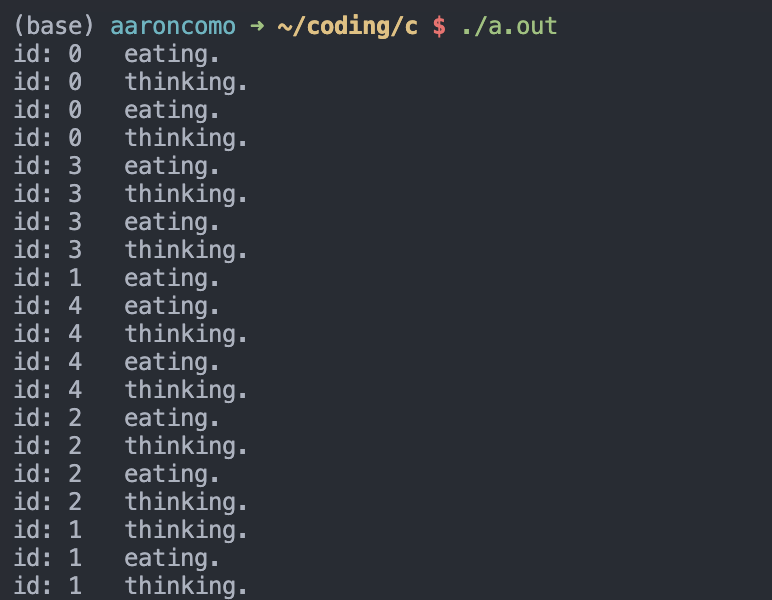
- 每个哲学家交替进行吃饭、思考
- 每个哲学家进行 2 轮
编写
pickup_forks()和return_forks函数1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
void pickup_forks(int id) { // 2k+1: right first, 2k: left first pthread_mutex_lock(&chopsticks[(id + direction[id % 2]) % 5]); pthread_mutex_lock(&chopsticks[(id + direction[id % 2 + 1] % 2) % 5]); printf("id: %d\teating.\n", id); } void return_forks(int id) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&chopsticks[(id + direction[id % 2 + 1] % 2) % 5]); pthread_mutex_unlock(&chopsticks[(id + direction[id % 2]) % 5]); printf("id: %d\tthinking.\n", id); }
- 奇数先拿右边
- 偶数先拿左边
- 防止同时拿起一边的筷子造成死锁
测试
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.