劫持系统调用表添加新系统调用
项目地址: github.com/AaronComo/OS-Assignment
核心步骤
如果想向系统中加入一个新的系统调用, 最常见的方法就是修改内核源码, 然后重新编译. 然而编译内核的过程很慢且内存开销极大, 仅仅为了加入一个系统调用就大动干戈编译整个内核, 说实话这是一个很浪费的过程. 这让我思考有没有方法能绕开编译就能加入新的调用.
网络上的方法千篇一律, 几乎全是使用 kallsyms_lookup_name 来查找 sys_call_table 但是这个函数早在 5.7 的版本就已经不再被导出. 在近些年发布的 Linux 上需要其他方法新增系统调用.
本文将提供一个新思路, 直接从运行时的内核中劫持 sys_call_table ,向其中插入新的系统调用.
其核心步骤如下:
- 通过已导出的方法
kprobe查找内核中不再导出的方法kallsyms_lookup_name - 使用函数指针指向
kallsyms_lookup_name函数的起始地址 - 使用c语言提供的
asm汇编指令将cr0寄存器的系统保护位 (第17位) 置0, 允许外部对内核的更改, 并记录寄存器原始值 - 通过
kallsyms_lookup_name找到sys_call_table的地址, 保存 335 号系统调用的原始函数地址 - 将 335 号调用更改为自己的系统调用
- 恢复
cr0的初始值
代码
劫持模块代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/unistd.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/kprobes.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("AaronComo");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Add a new system call to kernel without compiling it.");
MODULE_VERSION("1.0");
#define __NR_my_syscall 335
int orig_cr0;
unsigned long (*kallsyms_lookup_name_func)(const char *) = NULL; /* save the address of unexported kallsyms_lookup_name func */
unsigned long *sys_call_table = NULL; /* save sys_call_table */
void reset_cr0(unsigned int val); /* reset guard bit */
unsigned int set_cr0(void); /* alter guard bit to allow changes of sys_call_table, return cr0's original value */
void find_unexported(void); /* use kprobe to find unexported kernel function */
static int sys_my_syscall(void); /* declaration of self-defined func */
static int (*orig_syscall)(void); /* save original syscall of 335 */
unsigned int set_cr0(void) {
unsigned int cr0 = 0, ret;
asm volatile ("movq %%cr0, %%rax" : "=a"(cr0)); /* move original value of reg_cr0 to reg_rax and save it in cr0 */
ret = cr0;
cr0 &= 0xfffeffff; /* set 17th bit of cr0 to 0 */
asm volatile ("movq %%rax, %%cr0" :: "a"(cr0)); /* reg_rax=cr0, reg_cr0=reg_rax */
return ret;
}
void reset_cr0(unsigned int val) {
asm volatile ("movq %%rax, %%cr0" :: "a"(val));
}
void find_unexported(void) {
/**
* due to security policy, 'kallsyms_lookup_name' is no longer exported after 5.7
* use kprobe to export 'kallsyms_lookup_name'
*/
static struct kprobe kp = {
.symbol_name = "kallsyms_lookup_name"
};
int flag = -1;
flag = register_kprobe(&kp);
if (flag == -1) {
printk("fail to find kallsyms_lookup_name.\n");
}
if (kp.addr) {
printk("kallsyms_lookup_name: 0x%p\n", kp.addr);
kallsyms_lookup_name_func = (void *)kp.addr;
}
unregister_kprobe(&kp);
}
static int sys_my_syscall(void) {
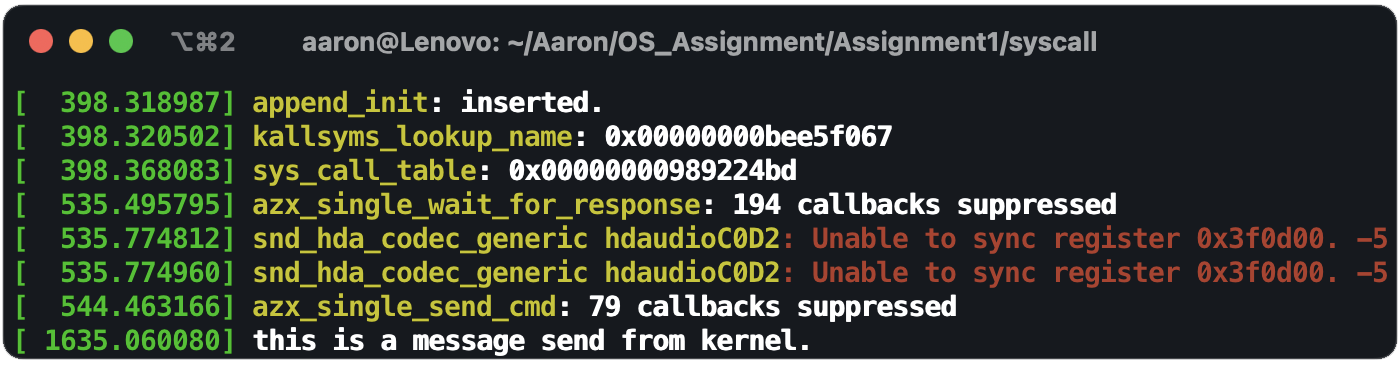
printk("this is a message send from kernel.\n");
return 335;
}
static int __init append_init(void) {
printk("%s: inserted.\n", __func__);
find_unexported();
sys_call_table = (unsigned long *)(*kallsyms_lookup_name_func)("sys_call_table");
printk("sys_call_table: 0x%p\n", sys_call_table);
orig_syscall = (int (*)(void))(sys_call_table[__NR_my_syscall]); /* save address of original syscall */
orig_cr0 = set_cr0();
sys_call_table[__NR_my_syscall] = (unsigned long)&sys_my_syscall;
reset_cr0(orig_cr0);
return 0;
}
static void __exit append_exit(void) {
orig_cr0 = set_cr0();
sys_call_table[__NR_my_syscall] = (unsigned long)orig_syscall;
reset_cr0(orig_cr0);
printk("%s: removed.\n", __func__);
}
module_init(append_init);
module_exit(append_exit);
测试代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
int main() {
int ret = syscall(335);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
安装模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
obj-m:= append_syscall.o
PWD:= $(shell pwd)
KERNELDIR:= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
EXTRA_CFLAGS= -O0
all:
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) clean
测试
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.